https://gitlab.com/ja4nm/quicksortFun fact: this implementation is actually a result of a bug I had in FERI urnik app when I was trying to sort list of object and I made a mistake in my comparison method. By the time I realised my mistake, this implementation was nearly done. Later I have done some benchmarks just for fun and I was actually quite surprised by the results.
QuickSort implementation in java which allows sorting List (List<T>) and arrays (T[]) of object in O(n log n) time. It also supports 4 types of pivot picking methods - FIRST_ELEMENT, LAST_ELEMENT, MEDIAN or MEDIAN_OF_THREE. For best performance MEDIAN or MEDIAN_OF_THREE is recommended.
More on pivot picking methods: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quicksort#Choice_of_pivot
Dummy monkey class for better understanding of examples below.
public class Monkey {
public String name;
public int bananaCapacity;
}
Sorting List of Monkey objects. Compare them by bananaCapacity and choose median as pivot.
ArrayList<Monkey> monkeys = //unordered ArrayList of Monkeys
QuickSort.sortList(monkeys, new QuickSort.Comparator<Monkey>() {
@Override
public int compare(Monkey a, Monkey b) {
if(a.bananaCapacity == b.bananaCapacity) return 0;
else if (a.bananaCapacity < b.bananaCapacity) return -1;
else return 1;
}
});
Sorting List of Monkey objects. Compare them by bananaCapacity and choose median of three as pivot.
ArrayList<Monkey> monkeys = //unordered ArrayList of monkeys
QuickSort.sortList(monkeys, QuickSort.PivotMethod.MEDIAN_OF_THREE, new QuickSort.Comparator<Monkey>() {
@Override
public int compare(Monkey a, Monkey b) {
if(a.bananaCapacity == b.bananaCapacity) return 0;
else if (a.bananaCapacity < b.bananaCapacity) return -1;
else return 1;
}
});
Sorting array of Monkey objects. Compare them by bananaCapacity and choose median of three as pivot.
Monkey[] monkeys = //unordered array of Monkeys
QuickSort.sortArray(monkeys, QuickSort.PivotMethod.MEDIAN_OF_THREE, new QuickSort.Comparator<Monkey>() {
@Override
public int compare(Monkey a, Monkey b) {
if(a.bananaCapacity == b.bananaCapacity) return 0;
else if (a.bananaCapacity < b.bananaCapacity) return -1;
else return 1;
}
});
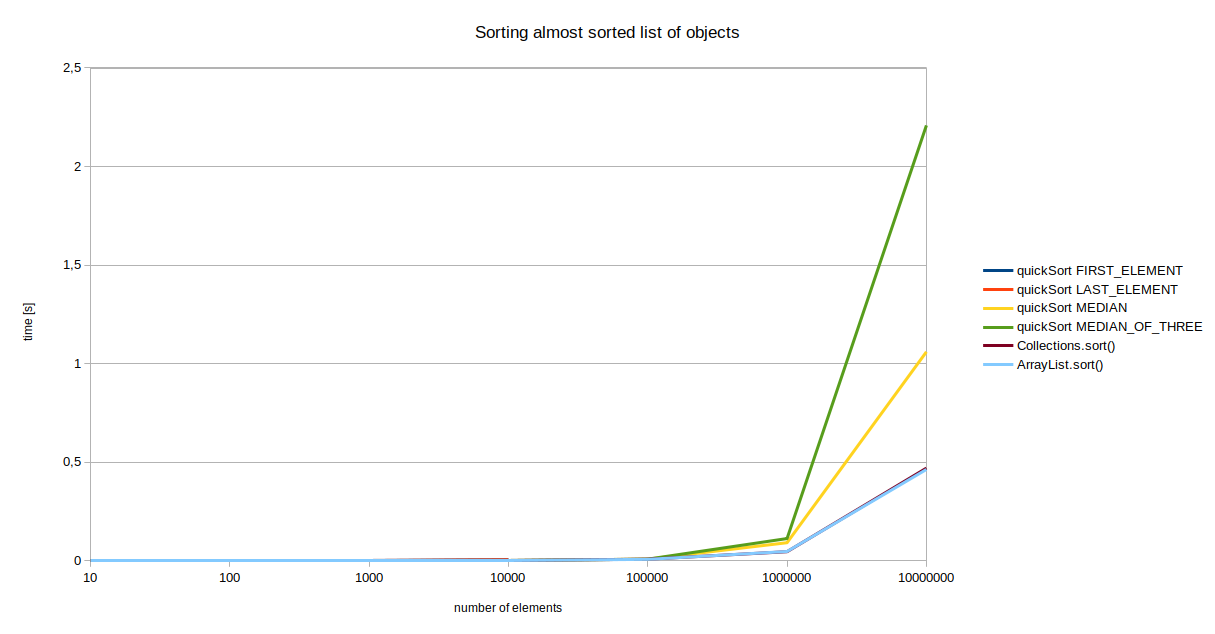
I have done some benchmarks of sorting different sizes and arangements of ArrayLists of Monkey objects. Benchmarks have been done on Intel i7-6700hq. All test cases have been created in advance and are the same for the same ArrayList size. Time unit is second.
ArrayList of Monkey objects.| no. of elements | qs FIRST_ELEMENT | qs LAST_ELEMENT | qs MEDIAN | qs MEDIAN_OF_THREE | Collections.sort() | ArrayList.sort() |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.001000 | 0.000000 |
| 100 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 1000 | 0.000667 | 0.000000 | 0.000333 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000333 |
| 10000 | 0.001333 | 0.001000 | 0.001333 | 0.001000 | 0.002667 | 0.002333 |
| 100000 | 0.015000 | 0.014667 | 0.014667 | 0.014667 | 0.021667 | 0.018667 |
| 1000000 | 0.253000 | 0.255000 | 0.250667 | 0.250667 | 0.266667 | 0.262667 |
| 10000000 | 3.905000 | 3.821333 | 3.638000 | 3.642333 | 4.016667 | 3.987000 |

ArrayList of Monkey objects.*Inappropriate pivot picking method results in a worst-case time complexity and the results are immeasurable. More: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quicksort#Worst-case_analysis
| no. of elements | qs FIRST_ELEMENT | qs LAST_ELEMENT | qs MEDIAN | qs MEDIAN_OF_THREE | Collections.sort() | ArrayList.sort() |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.000000 | 0.000333 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 100 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000333 | 0.000333 | 0.000333 | 0.000000 |
| 1000 | 0.000000 | 0.000333 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000333 | 0.000333 |
| 10000 | 0.004667 | 0.004333 | 0.001000 | 0.000667 | 0.000667 | 0.000667 |
| 100000 | * | * | 0.007667 | 0.007667 | 0.007333 | 0.006667 |
| 1000000 | * | * | 0.091000 | 0.112000 | 0.045333 | 0.046333 |
| 10000000 | * | * | 1.059333 | 2.208333 | 0.469333 | 0.462667 |